Updated: November 11, 2024
Form 8809 definition and meaning
Form 8809 allows businesses to apply to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) for a 30-day filing extension. However, only certain forms, such as W-2 and 1099, qualify for this extension, and the conditions can vary.
More about Form 8809 and its purpose
Businesses mandated to file information returns with the IRS must adhere to the set deadline, or they risk incurring penalties for noncompliance. However, the IRS offers some leniency by permitting businesses to request a 30-day filing extension using Form 8809, Application for Extension of Time To File Information Returns.
Form 8809 can be used to seek an extension for the following federal tax forms:
- W-2
- W-G2
- 1042-S
- 1094-C
- 1095
- 1097
- 1098
- 1099
- 3921
- 3922
- 5498
- 8027
Form 8809 cannot be used to request a filing extension for any forms not listed above, including those used for reporting both business and personal income tax returns.
It’s important to note that Form 8809 does not extend the deadline for furnishing tax statements to recipients. Instead, it merely grants businesses additional time to file the respective forms with the IRS.
Understanding the 30-day extension
When you submit Form 8809 to the IRS for many of the forms mentioned earlier, you’ll typically receive an automatic 30-day extension.
However, automatic extensions do not apply in the following cases:
- Forms W-2, 1099-NEC, 1099-QA, and 5498-QA.
- You already received an automatic extension and are seeking an additional 30 days.
In these cases, while you must still complete Form 8809 to request the extension, approval isn’t guaranteed. It will only be granted if you satisfy at least one of the following conditions:
- A catastrophic event in a federally declared disaster area prevented you from resuming operations or accessing essential records (like your accounting files).
- Your business operations were disrupted by a natural disaster, fire, or significant event.
- The person responsible for filing your information return encountered serious illness, was unavoidably absent, or passed away.
- Your business was in its first year of establishment.
- You didn’t obtain the essential payee data in time to accurately draft your information return.
If any of these criteria are met, you’ll receive the 30-day extension. However, further extensions beyond this won’t be available.
How to file Form 8809
You can request an extension from the IRS using the methods below, but be sure to note the exceptions.
- Online: Complete Form 8809 via the IRS’ FIRE System for an automatic 30-day extension. This method is not available for Forms W-2, 1099-NEC, 1099-QA, 5498-QA, or when requesting an additional 30-day extension.
- Electronically through the FIRE System: Ensure the file adheres to the specifications outlined in IRS Publication 1220.
- Paper: Fill out Form 8809 and mail it to the address provided in the “Where to file” section of the General Instructions for Form 8809.
For requests concerning Forms W-2, 1099-NEC, 1099-QA, 5498-QA, or an additional 30-day extension, you must submit via paper form and mail it to the IRS. For all other requests, the IRS encourages electronic submissions.
Though Form 8809 is concise, with only seven sections, its instructions are quite specific. Therefore, take the time to fill it out properly to prevent any processing delays.
What employers should know about Form 8809
- To request additional time to furnish statements, such as Form W-2s, to recipients, fax a letter to the IRS. Consult Publication 1220 for instructions on making this request.
- If you don’t file your information return on time and lack a valid extension, the IRS may impose a late penalty.
- To avoid the late filing penalty, seek a 30-day extension using Form 8809 (if applicable).
It’s important to submit Form 8809 by the respective deadline.
When to file Form 8809
The IRS advises submitting Form 8809 as soon as you realize an extension is necessary. However, the form cannot be filed prior to January 1 of the tax year for which the return is due. Any Form 8809 requests made after the deadline of the information return will not be approved by the IRS.
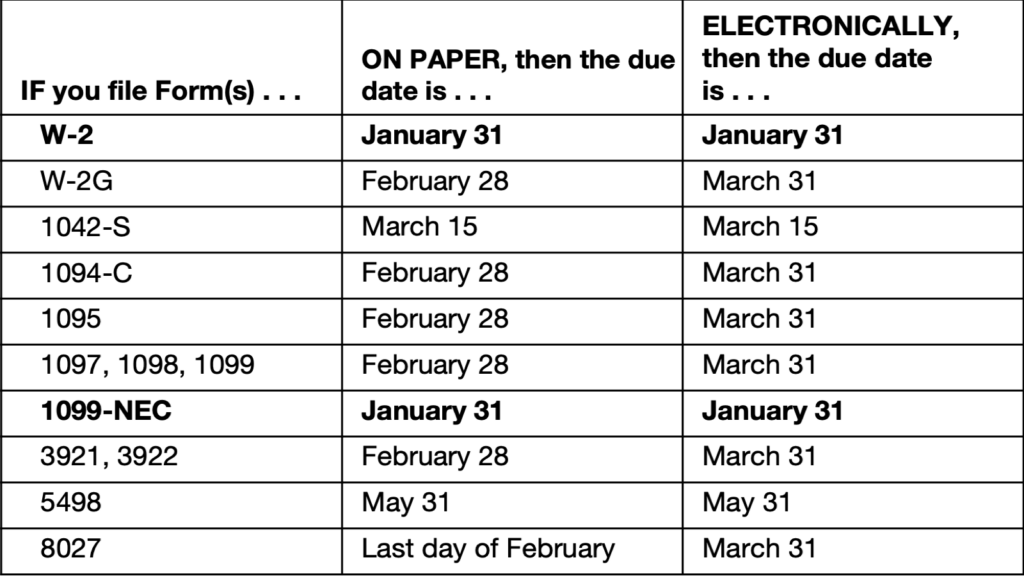
Here’s a chart from the IRS showing the due dates for Form 8809:
Using Form 8809 in a sentence
“I promptly filed Form 8809 with the IRS when I realized I couldn’t meet the filing deadline for my information return. This extension gave me an additional 30 days, allowing me to accurately complete and submit my return.”
Terms related to: Form 8809
Articles and resources related to: Form 8809

